How does ICT system work?
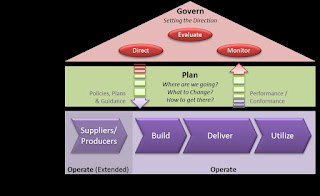
According to COBIT 5 framework, the ICT is composed with Governance, Planning, Building, and Running. Let’s use some analogues from automobile business to clarify the structure and functions of the ICT:
- The governance includes the ways of monitoring, evaluating and directing the actions. With automobile this means observing events around the car, breaking, accelerating and turning the steering wheel as assessed necessary.
- The planning includes the ways of anticipating the future: orientation, when and where to fill the tank, whom to give the ride, when to have service, etc.
- The building includes the ways and means to renew the ICT structure of technology, processes, and people either gradually part by part or at once by buying a new car.
- The running or delivering includes the operation of ICT systems according to processes accomplished by people to create value to the users. This means actually driving from one place to another and providing a reliable journey to the passengers.
- Then there is the actual utilization of ICT services i.e. Information management and for example situational awareness. Only the utilization leads into Information Superiority. From transportation business viewpoint this means that passengers are delivered safely on time to places they request with all their luggage intact.
How to drive the ICT system?
The governance of ICT is described in many best practices as ISO/IEC 38500, ISACA COBIT 5 (a framework for governance and management of enterprise IT), AXELOS ITIL v3 (a framework for IT service management), and TM Forum eTOM (a business process framework for digital enterprise). All of these models emphasize five key focus areas for governance: value creation, risk management, performance management, resource management, and strategic alignment.
Value
Value creation means that transportation creates added value to the passengers. They enjoy the swift and safe journey to where they want arriving fresh and ready to meet the actual reason for travelling. In ICT, this means that the end user perceives the added value of information, connectivity, situational awareness, and collaboration. The pre-expectations include that value is provided continuously (24/7) and sustaining the security where ever they choose to soldier. This means that the value creation chain is working smoothly. There are Service Catalogues that clearly set the expectations for ICT Services. There are Service Level Agreements between providers and users to establish trusted relationship. There are Operator Level Agreements to integrate several operators as value chains.
Risks
Risk management means that if there is an interruption during the drive, reserve car is ready to take the passengers on if the first car has a flat tire. There are also military police to escort the transportation and counter all security threats. In ICT language, this means that Availability and Information Security are optimized to provide reliable, confidential and assured ICT services to end users.
Performance
Performance management means that the transportation is fast enough to get there on time, the seat is good enough to feel comfortable, and there is water enough to compensate dehydration. In ICT language, performance means Quality of Service, Processing power, speed of transfer, Cost-Efficiency, and Flexibility.
Resources
Resource management means that the fleet of cars is maintained and inspected, drivers are well educated and licensed, and fuel stations are available. In ICT language, resources include human capital, material(HW), immaterial(SW), financial, organizational, and facility assets. These are the means that are used to create value through processes by using technical systems.
Strategic alignment
Strategic alignment implies that the fleet of cars is maintained at an optimal level providing Return of Investment but also expected the level of comfortable travelling experience, there is a differentiating value compared to competitors, and continuous development is keeping competitors catching up the advantage. In ICT language, strategic alignment means building and sustaining the information superiority over the enemy.
Your are ready to drive - how about some assisting features?
Once these five elements are in place, the actual governance is possible i.e. monitoring the status of all value chains, assessing the needs for a change, and directing the needed adjustment to either drive current or future goals. Planning can be supported by Capability portfolio, which balances risks, resources, investments, current operations and building the future capabilities. The other tool for planning is Architecture. Architecture is describing the structure (people, processes, and technology) from enterprise level down to single technical component level. Enterprise Architecture ensures that planning reflects strategic goals through business, information, and technology layers. A Target Architecture improves communication within development project and ensures that strategic goals and reference architecture guidance are followed.
