This is the second part of Host based information security and security operations in military digitized environment including example of survivable infrastructure and some ideas for signals training.
Figure 10: Example of survivable operation centre structure
Since Information, Processing, Communications services are separated from Staff elements they can be distributed through space of operation to create a C4I service network, which might be built according to private cloud computing architecture. Staff elements can be employed flexibly as collected under one shelter to optimize face to face cooperation, ordered to create task oriented command posts as situation requires (planning staff, forward command post) or be deployed in distributed way that no element is at same place at same time. Transferable staff elements may change place between shifts and increase further their non-detectability.
Figure 11: An example of staff element for distributed and transferable command structure
ICT in containers may be Commercial-Of-The-Shelf technology since end devices do not store any information but only provide a view to the presentation layer. All information and processing services are provided from C4I cloud thus element needs to be online to operate.
For example one shift of Security Operation Centre may be in one container and one place while doing their 9 hour shift. Second shift is being transferred to new location and will be on line one hour before shift change to insure proper handover. Third shift is on rest while this is happening in third place and in worst case can restore operational control within half an hour after being awakened.
Figure 12: An example of a fixed shelter for distributed data centre
Singular data centre should be restricted from cooling and floor space dimension not to allow asset grow too valuable at one location. Centre is sheltered from normal kinetic strike, but availability should be only medium level since number of parallel centres are providing required availability. Shelter should also provide electronic protection from both Electro Magnetic Pulse (EMP) and High Powered Microwave (HPM) strikes. One should not install in one centre nothing valuable that is not replicated elsewhere or is logically transferable within 30 minutes. This requires special logical configuration but current software defined cloud computing structures provide much easier high availability than earlier cluster structures.
Figure 13: Example of survivable ICT infrastructure
Access service is providing one layer of routing, roaming and accessing over several access networks. This is possible by using mobile IP and IPSEC VPN’s. Access networks should include both fixed, wireless accessed and mobile mediums that are used together to provide versatility and availability. For example to provide mobile access one may use WIFI-access within camp, larger cell access within normal patrolling area and SATCOM access in extreme terrain. Military access service provider should strive to maintain three possible accesses services available to client to provide required availability.
Fixed and sheltered data centres are distributed in the area of operation and connected with Core WAN. Together data centres create cloud computing infrastructure that allows replication of both data and process instances. There needs to be storage level distribution of data, data base level replication of data and possibly data item level of addressing and semantic driven distribution of data. Business logic should be divided to several virtual platforms so that there is possible to create both presentation domain and processing domain.
End devices are as thin as possible and from end user point of view zero configuration. There should be no major end user functions required when device roams between different access networks or user is transferring from fixed network to wireless accesses. End devices should be configured as terminals and all processing, storing and communication should be done within cloud. This restricts the area of vulnerability, lessens the host control and supports expendable user devices.
System operators and administrators should be identified at least with 3 separate factors. They should always access to role management level before allowing enter to actual applications level. Their work should be monitored and main tasks should be following process, where at least two persons are needed in sequence in order to execute task.
ICT system management and security management systems should be built to highest survivability and security level since they are essential for changes, business continuation and cyber defence thus main targets to opponent’s attacks.
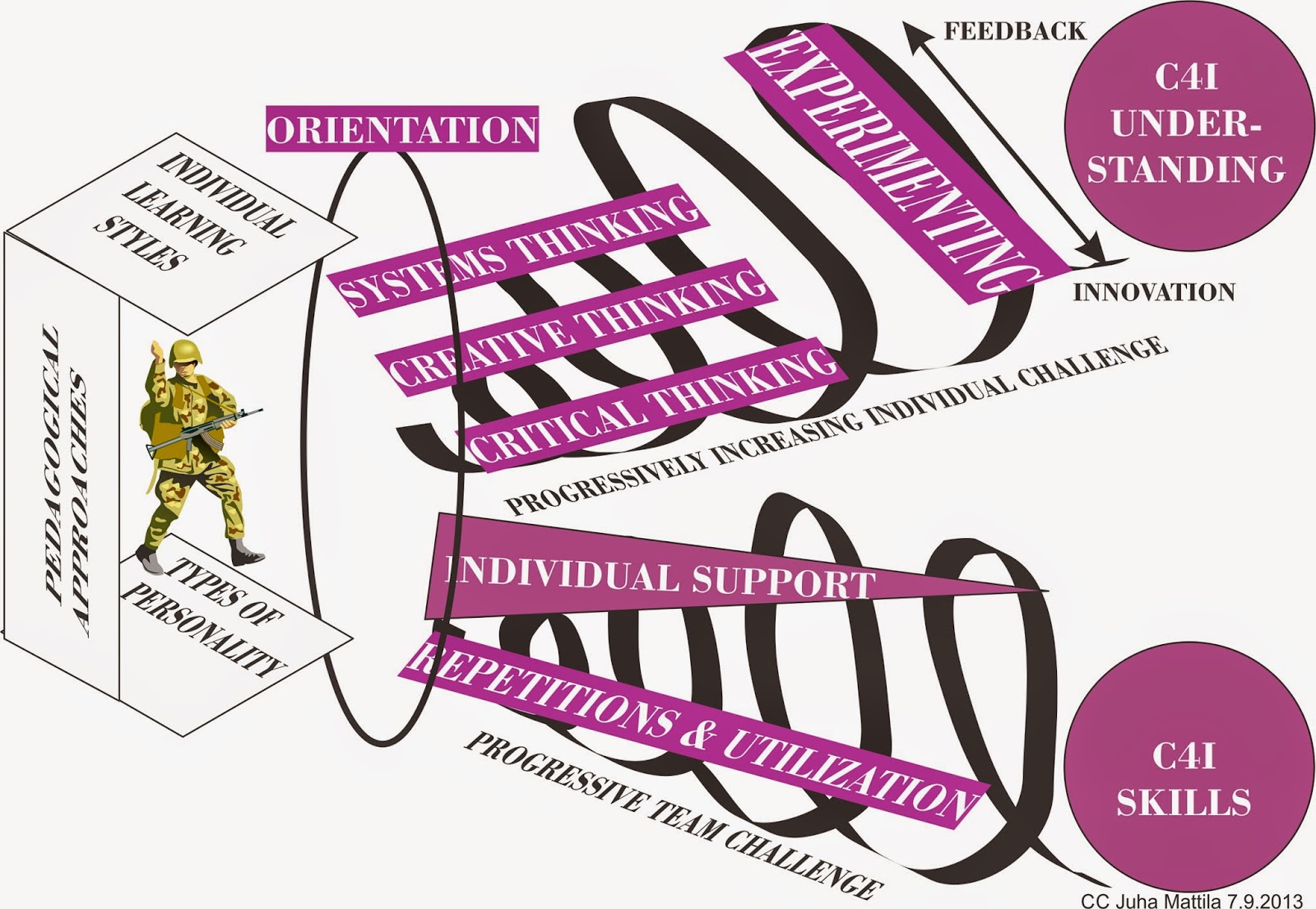
Figure 14: One orientation model for C4I understanding and skills training
Training of C4I soldiers starts always from individual. Training utilizes different pedagogical approaches adapted to individual learning styles and types of personality. Training has clear orientation structure that defines WHY coming skills and competence is needed. Deductive orientation also includes iterative introduction to features and countermeasures in C4I area of operation. Training for skills and understanding advance parallel and progressively providing possibilities for feedback, revisiting, extending further, digging deeper, room for innovation and mirroring with mentor.
C4I skills are learned mainly by team training with progressive challenges tailored to each team. Repetition is a discipline as a part of bigger system, but utilization of skills in different situations and environment is a driver for successful execution in progressively challenging environment. Although team is a unit in learning, individual support is very important during the first phases of instruction. According to individual maturity, support should be lessening as competence, innovation and teamwork are improving.
Training of C4I understanding is following Gartwright’s (2008) lines of educating soldiers rather how to think than what to think. This means introducing a combination of three thinking methods: systems thinking, creative thinking and critical thinking. These thinking tools should be utilized along individually tailored path of learning towards C4I understanding. This learning path is a spiral with feedback from subordinates, peers and instructors. Spiral curve is accelerated by windows of opportunity to utilize innovative solutions but by providing safe environment for mistakes. Experimentation is main driver and pedagogical method in training for long lasting understanding of C4I tasks, systems and area of operation.
To ensure individual and team function ability as a part of bigger entity and mainly in supportive position, training should be executed to standard. C4I standards should be defined from operations and exercises where fighting system of systems is being deployed. Mission-essential task list for C4I capabilities should be defined and systematically projected to each C4I functions of individuals, teams and systems. This adjustment spiral should continuously analyse level of troops and balancing requirements coming from ever extending spectrum of operations. Analytical adjustment spiral should provide C4I organizations with right cognitive framework and tangible measures, which have direct Impact on mission .
As any other military service or branch, C4I organizations should train as they fight. This means that training is done in team collective as soon as individual level is achieved. C4I troops operate the same system of systems but geographically separated. Co-operation in virtual world created by their C4I-system should be introduced early in their training. C4I teams work together with systems and other teams to provide services by following processes and driven by need of support of other arms and troops. C4I organizations should train always with some service to be provided to supportee in order to comprehend their interdependent role and be able to get pride from doing their support job well.
Since C4I organizations face opponent's effect directly in full spectrum of arsenal, their training conditions should include variants of environment, effects of opponent and changes of their supportee’s as gradually increased demands and problems closer resemblance of real world C4I area of operations includes. This demands skilful use of new training support methods like emulation, simulation and extended reality.
C4I teams should be trained to sustain spiritually, technically and functionally in harsh conditions, geographically separated from other troops, often attacked simultaneously by airborne weapons, electromagnetic waves and cyber measures. Spiritual sustenance requires team integrity that is built by close proximity with team members over 4 months of overcoming shared hardship, enjoying with shared achievements and sharing real world time with joys and sorrows. Technical sustenance requires soldiers to feel responsibility of their systems, maintain, supply and update them in order to keep services available. This is achieved by delegating the technical ownership of their systems, signal sites and vehicles to each team. Technical sustenance should be measured throughout training and not only during short exercises.
Functional sustenance requires fulfilling the individual and team role in larger system of systems. This needs habitual and reasoned obedience expressed in virtual collective like signals platoon, company or battalion. It also requires responsibility to fulfil one's role while facing lethal environment without capability to counter it any other way but indirectly by providing C4I services to other troops. To build this kind of discipline and culture from inside rather than outside needs mentoring, historical role models, appreciation and direct rewarding when appearing. When sole human being is weak in facing fears of battle, these collective codes of conduct come to support and make soldiers to fulfil their duty.
Training should be gradually more demanding driving towards set standards. C4I organization may structure their training in incremental sprints that consists learning phases as follows:
These sprints should be laminated over each other to ensure that mainstream training is based on increasingly familiar things. So each new subject or skill should be introduced via a sprint but in a coherent orientation framework. There should be different possibilities within sprint for each type of learning and personality to achieve most suitable learning path. Main exercise effort should be in application of C4I skills in different situations of facing effects of different variants of environment and opponent.
Figure 15: Signals and other C4I organization as part of bigger fighting system of systems in confrontation with similar chain of opponent's military force system.
Systems thinking in Signals and C4I means soldiers ability to identify their signal system as structure of technical and human social subsystems that are interrelated with each other while supporting greater fighting system of systems when confronting opponent's effects and system of systems. Soldiers should be able to explain the behaviour and interrelations between the parts of C4I system and cause-effect interactions with environment. Soldiers should be able to explain their C4I system behaviour and interaction within fighting system of systems and when effected by opponent's fighting system. Learning this needs individually optimized teaching environment, team thinking and reflection. Since interrelationships are costly to experiment in real world, new training support methods may provide major increase in impact on mission. When teaching systems thinking one should be aware of the following human features:
Creative thinking comes to use after capturing synthesis from systems thinking. There are many saying that creativity is not tolerated in hierarchical and paternalistic command and control system where constraints, discipline and supervision is typical. This is extremely distort perception of military leadership in Signals that is following guidelines of:
Creative thinking for Signals soldiers is best trained by solving a number of live world problems in simulated system of systems environment in co-operation with live stake holders. Virtual world should support collaboration between stake holders and these war game exercises should include different roles and role games to teach utilizing the diversity of people.
Critical thinking is supporting both systems and creative thinking tools in quest for Signals understanding. Every decision is based on assumptions – either known or non-aware. These assumptions must be recognised and critically studied, while implementing current decision. A side with implementing a plan, parallel optional plans should be produced to accelerate Command and Control process. When environment or opponent is not behaving in assumed way, leader must be able to reconsider earlier decisions and either adjust ongoing plan or replace it with more suitable plan. Here leaders should be aware of their natural tendency to have egocentric memory that forgets information that does not support adapted intent. Human being tends also to narrow one's thinking point of view with time and stress. As self-esteem improves there appears a tendency to feel superior based on own belief's rather than real world incidents. In the end human decision maker has a tendency not to notice facts or evidence contradicting one's beliefs or values.
Critical thinking skills are best developed in training by:
Together with C4I understanding leaders should have ability for timely decision making. There are many disadvantages in leaders, but major faults have been lack of decisiveness or integrity and inability to communicate. Signals leader should first formulate an intention of how C4I services will be supporting other troops and fighting system of systems. This intention should be communicated to all service providers within the value chain of signals as well as to supportees. Signals intention serves as a guide line for mission command, a reason for team’s efforts and a promise of service for supported troops. Other fragmentation decisions and orders may follow this initial decision, when needed to synchronize C4I system of systems operation.
Decision making is trained by making decisions and reflecting their outcomes. Taylor and Gollwitzer (1995) discovered that even in temporarily state of neuroticism, low sense of control or pessimism, it is better to make any decision and start implementing it. This will produce feeling of confidence and capability which further improves humans feeling of decisiveness. Similar approach for timely made decision was utilized in German officer training before WW II.
Decision making exercises should include trial – error – learning loops that enable leaders and soldiers to understand the causality of their decisions and give opportunities to learn from them. A sign of high level signals leader is that he learns from his mistakes, owns his failures and their outcomes, remedies and rectifies unwanted outcomes and puts safeguards in place to prevent their recurrence.
Continuous improvement
Since all Signals and C4I organizations skills and understanding is relative to opponent’s capabilities and depends on changing environment, technology and supportees, there are no fixed goals but continuous learning of new skills and understanding within C4I organizations. This is achieved by following LEAN principles of continuous improvement and Capability Maturity Model (CMM) to define performance of processes through organizations.
LEAN development is developed by Taiichi Ohno in Toyota to get rid of muda, ‘waste’ that any human activity has tendency to build around functions within time. This waste absorbs resources but creates no value. Lean thinking requires to define value, stream, flow, pull and establish continuous perfection. Value is reason for existence. It is the information and services Signals is producing to other services. Then one has to understand the value stream, which is a set of specific actions required to produce C4I service. Flow includes all necessary functions and organization that is needed to produce C4I services. There is a pull of need coming from actual end users and supported organizations. Lastly there is the continuous perfection, where users pull value as continuous flow through the whole value stream. Measures should be attached along this model to give direct feedback both for operators and leaders to improve their production, protection and maintenance of C4I services.
With Capability Maturity Model Signals and C4I organizations are understanding how their service providing and managing processes are maturing step by step. Since Signals and other C4I organizations are producing value mainly with processes, it is important to understand how the culture of man-machine-process system matures through following steps:
Together with understanding of process culture maturity and of continuous improvement of value creating, Signals and C4I organizations keep up with opponent’s countermeasures, changing environment and demanding client.
Continuous exercising of BLUE – RED struggle
Since military C4I structures are mainly isolated from every day attacks of Internet, they are living in peace behind high perimeter Firewalls and air gaps. Within their digital fortifications there are only well behaving end users and very clandestine opponents. Signals and C4I service production organizations do not get practice enough to improve their skills and understanding. Thus cyber exercises are normal routine in digital environment. Opponent’s behaviour and deeds are simulated by Red teams that execute advanced attacks, physical destruction and electromagnetic effects. These controlled event provide C4I personnel needed stimulus to cooperate and learn to achieve better in difficult situations.
Since no one can defend successfully alone for long in digital environment, national exercises should be introduced to improve cooperation between organizations security operations, national CERT agencies, information service providers, application service providers and communication service providers. These exercises should be executed both as wargaming and practical domain defence way.
National exercises are not enough, but C4I crews are to participate also International exercises, where, in cooperation with other nations, sharing of experiences and practicing innovative attacks and improving defensive tactics happens. These exercises are for example:
When planning and preparing for confrontation in digitized environment, one should see beyond systems and cyber to whole digitized global entity with strong social networks and several other connections that opponent may use as avenue of attack.
In military operations, cyber is only a part of whole picture although one of the newest dimensions in area of operations. Focusing mainly to cyber dimension and contemporary crises, one may reach only partial or narrow conclusions.
To be able to defend oneself successfully, one needs to understand opponent’s strategy, operational possibilities and tactical means. Defence is always defined to protect valuable assets against most threatening attacks. Otherwise there is a tendency to try to protect everything and end up protecting nothing, since defence is spread too thinly.
If threat in public Internet has evolved from experimental hackering of early days to professional criminals trying to steal valuable information and states and large organizations to gain advantages, military rationale is to wage information operations, prepare for other means of attacks and shock and awe in the very beginning of operation.
Human being and its trust is still main target for opponent that is planning cost-effective operations. Analysing owns trust-structure will expose most valuable targets of one’s opponent but also center of gravity that should be protected. Planning attack is also part of planning defence.
In military digital environment method of protecting and securing assets is evolving from building domain perimeter security measures towards installing firewalls on every host in domain and monitoring all behaviour between hosts. Successful defence demands quick reaction forces to take down malevolent processes, which means tighter integration between all ICT service provider organizations and their support chain.
As complexity, velocity and volume of digital domains increases, it becomes hard to detect anomalies. Depth of defence is built by improving intelligence, building multilevel protection and adding depth between possible avenues of advance and most valued assets.
Even though big data analysis is improving sense making, there is a need to be a part of society of other defenders to learn quicker from other’s mistakes and experiences. Versatility of attacks is increasing and it is impossible for any one organization to be sufficient at all levels of technology and their possible malevolent exploitation.
Reactive defence does not produce advantage over attacker, but more proactive measures must be utilized. This may begin with vulnerability testing and hardening but go further to design more defendable ICT system structures. There are also self-healing functions and software defined security available to modify digital environment friendlier for defence.
Since command and control of security and ICT operations become essential for defence, it also becomes one of the main targets for opponent. Management system is attacked both cyber, physical, electromagnetic and psychological means. Protection against these measures should be defined according mission and space of operation specific analysis.
If one builds defence capabilities mainly based on programmed automatic executed by machines, it becomes itself a vulnerability that opponent may exploit. There is a need of high skilled and knowledgeable people and processes that integrate people’s deeds together in defence of digitalized environment. As automated machines also automated people are vulnerability so focus should be also in understanding and situational based behaviour.
It takes lot of training and exercises to build mature skills and understanding. It also requires to enable people to confront different situations and different ideas to continuously improve their skills. Defence capability in digitalized environment is relative to opponents capabilities thus right intelligence and scenario analyses is needed to build protection to sufficient level.
3. SURVIVABLE OPERATION CENTRE INFRASTUCTURE
Surviving under kinetic strike
Assets distribution and transferability are main means of survivability in area of operations, where missile attacks, special operation forces and information operations are main means that opponent might be using against ICT infrastructure. Since Command and Control and system management centres are opponent’s main targets, they should be protected unless seamless dominance in air defence and perimeter defence is sustained. First principle of survivable architecture is to separate people centres from data centres since both gain more from specific protection. Staff and their facilities may be fixed, transferable or mobile, but data centres should be sheltered in fixed facilities since amount of information is too large to be replicated on demand. Figure 10 is depicting a concept for survivable operation centre structure, where people are divided into several smaller staff elements, which are transferable or mobile and may be distributed or collected according to threat or mission.Figure 10: Example of survivable operation centre structure
Since Information, Processing, Communications services are separated from Staff elements they can be distributed through space of operation to create a C4I service network, which might be built according to private cloud computing architecture. Staff elements can be employed flexibly as collected under one shelter to optimize face to face cooperation, ordered to create task oriented command posts as situation requires (planning staff, forward command post) or be deployed in distributed way that no element is at same place at same time. Transferable staff elements may change place between shifts and increase further their non-detectability.
Staff elements
Staff is operating divided into operation centre elements that take and sustain a crew of five staff officers. They are working for example in 20 feet container, which is transferable both on sea, air and ground. When collected together containers may be piled together and each above one other under single shelter. Unloading a container and preparing it to be operational should not take more than 15 minutes. If one requires to deliver decoys, it is easy to deploy similar sea containers with some heat and electromagnetic radiation source. Concept is depicted in figure 11.Figure 11: An example of staff element for distributed and transferable command structure
ICT in containers may be Commercial-Of-The-Shelf technology since end devices do not store any information but only provide a view to the presentation layer. All information and processing services are provided from C4I cloud thus element needs to be online to operate.
For example one shift of Security Operation Centre may be in one container and one place while doing their 9 hour shift. Second shift is being transferred to new location and will be on line one hour before shift change to insure proper handover. Third shift is on rest while this is happening in third place and in worst case can restore operational control within half an hour after being awakened.
Sheltering Data centres
Military management system requires data centres and since the amount of information denies to carry them with transferable or mobile staffs, they are well sheltered in fixed, distributed sites with volume relative to opponent’s power of effect. Data centres do create together a cloud computing structure which allows data and services be flowing or transferring between data centres. One shelter for data centre is depicted in figure 12.Figure 12: An example of a fixed shelter for distributed data centre
Singular data centre should be restricted from cooling and floor space dimension not to allow asset grow too valuable at one location. Centre is sheltered from normal kinetic strike, but availability should be only medium level since number of parallel centres are providing required availability. Shelter should also provide electronic protection from both Electro Magnetic Pulse (EMP) and High Powered Microwave (HPM) strikes. One should not install in one centre nothing valuable that is not replicated elsewhere or is logically transferable within 30 minutes. This requires special logical configuration but current software defined cloud computing structures provide much easier high availability than earlier cluster structures.
Surviving from logical attacks
The logical structure of ICT infrastructure is protecting both from physical and logical attacks. Defendable ICT infrastructure is illustrated in figure 13. Network level is divided into two main purposes: Core production network and Access networks. Core network is more stable, but very connected network with high performance links between data centres. Around data centre there should be one or two rings of physical cabling and at least layer 2 rerouting to restore connection after several cable cuts.Figure 13: Example of survivable ICT infrastructure
Access service is providing one layer of routing, roaming and accessing over several access networks. This is possible by using mobile IP and IPSEC VPN’s. Access networks should include both fixed, wireless accessed and mobile mediums that are used together to provide versatility and availability. For example to provide mobile access one may use WIFI-access within camp, larger cell access within normal patrolling area and SATCOM access in extreme terrain. Military access service provider should strive to maintain three possible accesses services available to client to provide required availability.
Fixed and sheltered data centres are distributed in the area of operation and connected with Core WAN. Together data centres create cloud computing infrastructure that allows replication of both data and process instances. There needs to be storage level distribution of data, data base level replication of data and possibly data item level of addressing and semantic driven distribution of data. Business logic should be divided to several virtual platforms so that there is possible to create both presentation domain and processing domain.
End devices are as thin as possible and from end user point of view zero configuration. There should be no major end user functions required when device roams between different access networks or user is transferring from fixed network to wireless accesses. End devices should be configured as terminals and all processing, storing and communication should be done within cloud. This restricts the area of vulnerability, lessens the host control and supports expendable user devices.
System operators and administrators should be identified at least with 3 separate factors. They should always access to role management level before allowing enter to actual applications level. Their work should be monitored and main tasks should be following process, where at least two persons are needed in sequence in order to execute task.
ICT system management and security management systems should be built to highest survivability and security level since they are essential for changes, business continuation and cyber defence thus main targets to opponent’s attacks.
4. BUILDING REQUIRED COMPETENCE AND SKILLS
Key competence and skills of Signals and C4I organizations
Following picture is describing a learning orientation model for Command, Control, Communications, Computers and Information (C4I) skills and understanding.Figure 14: One orientation model for C4I understanding and skills training
Training of C4I soldiers starts always from individual. Training utilizes different pedagogical approaches adapted to individual learning styles and types of personality. Training has clear orientation structure that defines WHY coming skills and competence is needed. Deductive orientation also includes iterative introduction to features and countermeasures in C4I area of operation. Training for skills and understanding advance parallel and progressively providing possibilities for feedback, revisiting, extending further, digging deeper, room for innovation and mirroring with mentor.
C4I skills are learned mainly by team training with progressive challenges tailored to each team. Repetition is a discipline as a part of bigger system, but utilization of skills in different situations and environment is a driver for successful execution in progressively challenging environment. Although team is a unit in learning, individual support is very important during the first phases of instruction. According to individual maturity, support should be lessening as competence, innovation and teamwork are improving.
Training of C4I understanding is following Gartwright’s (2008) lines of educating soldiers rather how to think than what to think. This means introducing a combination of three thinking methods: systems thinking, creative thinking and critical thinking. These thinking tools should be utilized along individually tailored path of learning towards C4I understanding. This learning path is a spiral with feedback from subordinates, peers and instructors. Spiral curve is accelerated by windows of opportunity to utilize innovative solutions but by providing safe environment for mistakes. Experimentation is main driver and pedagogical method in training for long lasting understanding of C4I tasks, systems and area of operation.
Learning C4I skills
C4I training should provide optimal support to learn team skills in a disciplinary way to ensure that fighting system of systems is operating effectively and persistently. C4I skills include:- Individual ability to operate and admin C4I devices, while sustaining in area of operation;
- Team ability to accomplish more together as a part of C4I system when operating in C4I area of operation;
- Co-operation ability of teams to provide services in disciplined way with complex C4I-system of systems in volatile and harsh environment.
To ensure individual and team function ability as a part of bigger entity and mainly in supportive position, training should be executed to standard. C4I standards should be defined from operations and exercises where fighting system of systems is being deployed. Mission-essential task list for C4I capabilities should be defined and systematically projected to each C4I functions of individuals, teams and systems. This adjustment spiral should continuously analyse level of troops and balancing requirements coming from ever extending spectrum of operations. Analytical adjustment spiral should provide C4I organizations with right cognitive framework and tangible measures, which have direct Impact on mission .
As any other military service or branch, C4I organizations should train as they fight. This means that training is done in team collective as soon as individual level is achieved. C4I troops operate the same system of systems but geographically separated. Co-operation in virtual world created by their C4I-system should be introduced early in their training. C4I teams work together with systems and other teams to provide services by following processes and driven by need of support of other arms and troops. C4I organizations should train always with some service to be provided to supportee in order to comprehend their interdependent role and be able to get pride from doing their support job well.
Since C4I organizations face opponent's effect directly in full spectrum of arsenal, their training conditions should include variants of environment, effects of opponent and changes of their supportee’s as gradually increased demands and problems closer resemblance of real world C4I area of operations includes. This demands skilful use of new training support methods like emulation, simulation and extended reality.
C4I teams should be trained to sustain spiritually, technically and functionally in harsh conditions, geographically separated from other troops, often attacked simultaneously by airborne weapons, electromagnetic waves and cyber measures. Spiritual sustenance requires team integrity that is built by close proximity with team members over 4 months of overcoming shared hardship, enjoying with shared achievements and sharing real world time with joys and sorrows. Technical sustenance requires soldiers to feel responsibility of their systems, maintain, supply and update them in order to keep services available. This is achieved by delegating the technical ownership of their systems, signal sites and vehicles to each team. Technical sustenance should be measured throughout training and not only during short exercises.
Functional sustenance requires fulfilling the individual and team role in larger system of systems. This needs habitual and reasoned obedience expressed in virtual collective like signals platoon, company or battalion. It also requires responsibility to fulfil one's role while facing lethal environment without capability to counter it any other way but indirectly by providing C4I services to other troops. To build this kind of discipline and culture from inside rather than outside needs mentoring, historical role models, appreciation and direct rewarding when appearing. When sole human being is weak in facing fears of battle, these collective codes of conduct come to support and make soldiers to fulfil their duty.
Training should be gradually more demanding driving towards set standards. C4I organization may structure their training in incremental sprints that consists learning phases as follows:
- Orientation and basics,
- Function as system with repetition,
- Function as system of systems.
These sprints should be laminated over each other to ensure that mainstream training is based on increasingly familiar things. So each new subject or skill should be introduced via a sprint but in a coherent orientation framework. There should be different possibilities within sprint for each type of learning and personality to achieve most suitable learning path. Main exercise effort should be in application of C4I skills in different situations of facing effects of different variants of environment and opponent.
Learning Signals understanding
Signals understanding is leader’s and administrator’s ability to perceive their space of operation, teams and systems, other combat supporters, supportees and opponent as huge system where different parts interact with each other and with environment. It requires C4I soldiers to achieve synthesis when processing towards understanding of this phenomena. C4I soldiers should reach the level of insight and foresight to be able to innovate and create best ways to deploy and operate one's C4I-system as interdependent part of fighting system of systems. Creativity is not enough since human behavioural weaknesses, but must be balanced with critical thinking and timely decision making. This understanding is needed from team leader level to highest C4I system, Chief Information Officer, Signals Commander or Head of J6 levels. Figure 15 tries to capture some features in Signals area of operation.Figure 15: Signals and other C4I organization as part of bigger fighting system of systems in confrontation with similar chain of opponent's military force system.
Systems thinking in Signals and C4I means soldiers ability to identify their signal system as structure of technical and human social subsystems that are interrelated with each other while supporting greater fighting system of systems when confronting opponent's effects and system of systems. Soldiers should be able to explain the behaviour and interrelations between the parts of C4I system and cause-effect interactions with environment. Soldiers should be able to explain their C4I system behaviour and interaction within fighting system of systems and when effected by opponent's fighting system. Learning this needs individually optimized teaching environment, team thinking and reflection. Since interrelationships are costly to experiment in real world, new training support methods may provide major increase in impact on mission. When teaching systems thinking one should be aware of the following human features:
- Human being has tendency of thinking self-delusional and wishful while avoiding real world friction and unpleasant issues
- One should focus on the purpose for which a system was created more than only processes and procedures of the system.
- Simple use cases are not enough to achieve insight. One must experiment over time in seeking patterns and feedback loops to find rules of dynamics of a complex system.
- Thinking should be focusing on synthesis over analysis – understanding whole over parts.
- Leaders have a tendency to neglect systems thinking when in hurry, when they are focusing short-time goals or when their self-perception is too strong.
- Technically oriented leaders have tendency to focus only technical system interrelations where as human oriented leaders might be more focused on social interrelations. Both approaches are needed in understanding C4I system of systems in its space of operation.
Creative thinking comes to use after capturing synthesis from systems thinking. There are many saying that creativity is not tolerated in hierarchical and paternalistic command and control system where constraints, discipline and supervision is typical. This is extremely distort perception of military leadership in Signals that is following guidelines of:
- Approaching problem always from different scenarios and war gaming their possible out-come before deciding, which course of action should be taken as a best option to succeed in mission.
- Including technical specialists and military generalists into planning process for better synthesis of whole situation and tactical options for signals
- Learning continuously from lessons identified and especially capturing applicable ideas from those outside Signals business.
- Making timely decision and bearing the responsibility of action in face of troops, commander, supportees and oneself.
- Giving order in form of missions rather than tasks to give room for subordinate’s creativity, although securing that everyone dependent on synchronization is aware of changes.
- Always thinking from opponent's point of view and not being unnecessarily evident in signals or C4I tactics.
- Understanding that opponent's commanders are also creative beings and strive for surprise, capturing initiative and shaking their opponent's system of systems.
Creative thinking for Signals soldiers is best trained by solving a number of live world problems in simulated system of systems environment in co-operation with live stake holders. Virtual world should support collaboration between stake holders and these war game exercises should include different roles and role games to teach utilizing the diversity of people.
Critical thinking is supporting both systems and creative thinking tools in quest for Signals understanding. Every decision is based on assumptions – either known or non-aware. These assumptions must be recognised and critically studied, while implementing current decision. A side with implementing a plan, parallel optional plans should be produced to accelerate Command and Control process. When environment or opponent is not behaving in assumed way, leader must be able to reconsider earlier decisions and either adjust ongoing plan or replace it with more suitable plan. Here leaders should be aware of their natural tendency to have egocentric memory that forgets information that does not support adapted intent. Human being tends also to narrow one's thinking point of view with time and stress. As self-esteem improves there appears a tendency to feel superior based on own belief's rather than real world incidents. In the end human decision maker has a tendency not to notice facts or evidence contradicting one's beliefs or values.
Critical thinking skills are best developed in training by:
- Providing knowledge from a multidisciplinary perspective about critical thinking skills by providing legends of different tactical decisions and their outcomes,
- Practicing the recognition of assumptions in C4I and Signals context and environment
- Reflecting situation in every debriefing from egocentric approach in dialogue with peers or with instructor that may play role of “devil’s advocate”.
Together with C4I understanding leaders should have ability for timely decision making. There are many disadvantages in leaders, but major faults have been lack of decisiveness or integrity and inability to communicate. Signals leader should first formulate an intention of how C4I services will be supporting other troops and fighting system of systems. This intention should be communicated to all service providers within the value chain of signals as well as to supportees. Signals intention serves as a guide line for mission command, a reason for team’s efforts and a promise of service for supported troops. Other fragmentation decisions and orders may follow this initial decision, when needed to synchronize C4I system of systems operation.
Decision making is trained by making decisions and reflecting their outcomes. Taylor and Gollwitzer (1995) discovered that even in temporarily state of neuroticism, low sense of control or pessimism, it is better to make any decision and start implementing it. This will produce feeling of confidence and capability which further improves humans feeling of decisiveness. Similar approach for timely made decision was utilized in German officer training before WW II.
Decision making exercises should include trial – error – learning loops that enable leaders and soldiers to understand the causality of their decisions and give opportunities to learn from them. A sign of high level signals leader is that he learns from his mistakes, owns his failures and their outcomes, remedies and rectifies unwanted outcomes and puts safeguards in place to prevent their recurrence.
Continuous improvement
Since all Signals and C4I organizations skills and understanding is relative to opponent’s capabilities and depends on changing environment, technology and supportees, there are no fixed goals but continuous learning of new skills and understanding within C4I organizations. This is achieved by following LEAN principles of continuous improvement and Capability Maturity Model (CMM) to define performance of processes through organizations.
LEAN development is developed by Taiichi Ohno in Toyota to get rid of muda, ‘waste’ that any human activity has tendency to build around functions within time. This waste absorbs resources but creates no value. Lean thinking requires to define value, stream, flow, pull and establish continuous perfection. Value is reason for existence. It is the information and services Signals is producing to other services. Then one has to understand the value stream, which is a set of specific actions required to produce C4I service. Flow includes all necessary functions and organization that is needed to produce C4I services. There is a pull of need coming from actual end users and supported organizations. Lastly there is the continuous perfection, where users pull value as continuous flow through the whole value stream. Measures should be attached along this model to give direct feedback both for operators and leaders to improve their production, protection and maintenance of C4I services.
With Capability Maturity Model Signals and C4I organizations are understanding how their service providing and managing processes are maturing step by step. Since Signals and other C4I organizations are producing value mainly with processes, it is important to understand how the culture of man-machine-process system matures through following steps:
- “Initial (chaotic, ad hoc, individual heroics) - the starting point for use of a new or undocumented repeat process.
- Repeatable - the process is at least documented in way that repeating the same steps may be attempted.
- Defined - the process is defined/confirmed as a standard business process, and decomposed to levels 0, 1 and 2 (the last being Work Instructions).
- Managed - the process is quantitatively managed in accordance with agreed-upon metrics.
- Optimizing - process management includes deliberate process optimization/improvement.”
Together with understanding of process culture maturity and of continuous improvement of value creating, Signals and C4I organizations keep up with opponent’s countermeasures, changing environment and demanding client.
Continuous exercising of BLUE – RED struggle
Since military C4I structures are mainly isolated from every day attacks of Internet, they are living in peace behind high perimeter Firewalls and air gaps. Within their digital fortifications there are only well behaving end users and very clandestine opponents. Signals and C4I service production organizations do not get practice enough to improve their skills and understanding. Thus cyber exercises are normal routine in digital environment. Opponent’s behaviour and deeds are simulated by Red teams that execute advanced attacks, physical destruction and electromagnetic effects. These controlled event provide C4I personnel needed stimulus to cooperate and learn to achieve better in difficult situations.
Since no one can defend successfully alone for long in digital environment, national exercises should be introduced to improve cooperation between organizations security operations, national CERT agencies, information service providers, application service providers and communication service providers. These exercises should be executed both as wargaming and practical domain defence way.
National exercises are not enough, but C4I crews are to participate also International exercises, where, in cooperation with other nations, sharing of experiences and practicing innovative attacks and improving defensive tactics happens. These exercises are for example:
- Multinational Experiment (MNE) which is both operations and C4I concept development experimentation to improve international peace and stability operations capabilities.
- NATO Coalition Warrior Interoperability exploration, experimentation, examination exercise (CWIX) is annual exercise where multinational C4I systems, processes and competence is exercised as larger entity including cyber attack and defence.
- USEUCOM/NATO Combined Endeavour (CE) is the largest command, control, communications and computers interoperability event in the world. In event hundreds of C4I professionals conduct series of operationally-focused interoperability tests to achieve multinational interoperability required in ongoing and future operations. There is also Cyber Endeavour which is professional seminar in tactical level cyber defence and offence.
- NATO Cooperative Cyber Defence, Centre of Excellence arranges annual Locked Shields real-time network defence exercise.
Conclusion
Although military often has several separate ICT domains that are even separated from each other with air gap at network level, there are other means for avenues of attacks. Insiders, social networks, electricity, conduction of electromagnetic fields, kinetic effect in physical dimension, supply of SW or HW, etc. This exposes military ICT structures to three classical vulnerabilities of fortifications: enemy is already inside, enemy is beating you by destroying your logistics or adversary is using dimension that is outside of defenders imagination.When planning and preparing for confrontation in digitized environment, one should see beyond systems and cyber to whole digitized global entity with strong social networks and several other connections that opponent may use as avenue of attack.
In military operations, cyber is only a part of whole picture although one of the newest dimensions in area of operations. Focusing mainly to cyber dimension and contemporary crises, one may reach only partial or narrow conclusions.
To be able to defend oneself successfully, one needs to understand opponent’s strategy, operational possibilities and tactical means. Defence is always defined to protect valuable assets against most threatening attacks. Otherwise there is a tendency to try to protect everything and end up protecting nothing, since defence is spread too thinly.
If threat in public Internet has evolved from experimental hackering of early days to professional criminals trying to steal valuable information and states and large organizations to gain advantages, military rationale is to wage information operations, prepare for other means of attacks and shock and awe in the very beginning of operation.
Human being and its trust is still main target for opponent that is planning cost-effective operations. Analysing owns trust-structure will expose most valuable targets of one’s opponent but also center of gravity that should be protected. Planning attack is also part of planning defence.
In military digital environment method of protecting and securing assets is evolving from building domain perimeter security measures towards installing firewalls on every host in domain and monitoring all behaviour between hosts. Successful defence demands quick reaction forces to take down malevolent processes, which means tighter integration between all ICT service provider organizations and their support chain.
As complexity, velocity and volume of digital domains increases, it becomes hard to detect anomalies. Depth of defence is built by improving intelligence, building multilevel protection and adding depth between possible avenues of advance and most valued assets.
Even though big data analysis is improving sense making, there is a need to be a part of society of other defenders to learn quicker from other’s mistakes and experiences. Versatility of attacks is increasing and it is impossible for any one organization to be sufficient at all levels of technology and their possible malevolent exploitation.
Reactive defence does not produce advantage over attacker, but more proactive measures must be utilized. This may begin with vulnerability testing and hardening but go further to design more defendable ICT system structures. There are also self-healing functions and software defined security available to modify digital environment friendlier for defence.
Since command and control of security and ICT operations become essential for defence, it also becomes one of the main targets for opponent. Management system is attacked both cyber, physical, electromagnetic and psychological means. Protection against these measures should be defined according mission and space of operation specific analysis.
If one builds defence capabilities mainly based on programmed automatic executed by machines, it becomes itself a vulnerability that opponent may exploit. There is a need of high skilled and knowledgeable people and processes that integrate people’s deeds together in defence of digitalized environment. As automated machines also automated people are vulnerability so focus should be also in understanding and situational based behaviour.
It takes lot of training and exercises to build mature skills and understanding. It also requires to enable people to confront different situations and different ideas to continuously improve their skills. Defence capability in digitalized environment is relative to opponents capabilities thus right intelligence and scenario analyses is needed to build protection to sufficient level.





No comments:
Post a Comment